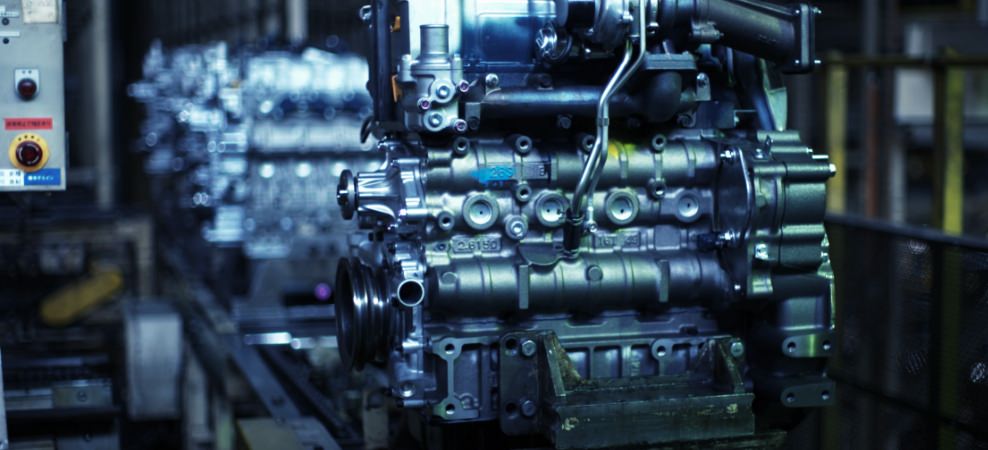
Assembly
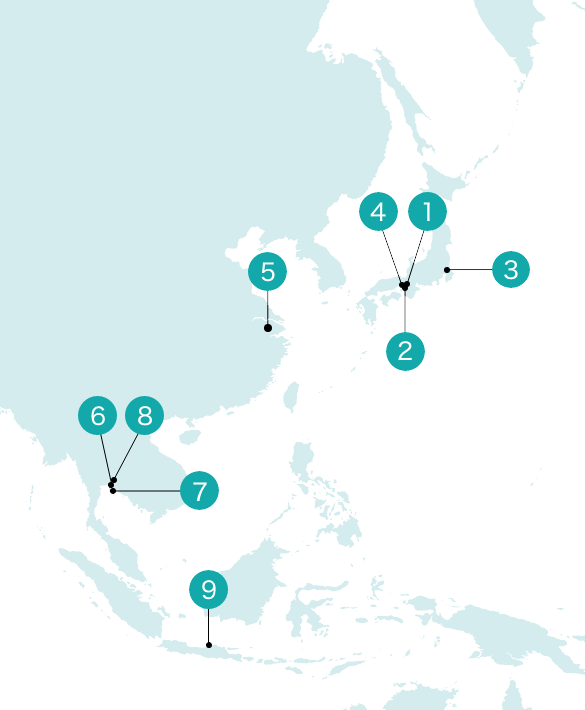
A Unique Assembly Production System that Assembles Engines with Different Specifications in a Single Line
Engines with the same specifications are typically produced on the same assembly line.
We have designed the Kubota engine assembly line based on a different concept.
This concept calls for assembling multiple engines with different specifications on a single line.
Kubota Engine routinely produces 2,000 or more engines simultaneously, while also responding quickly to fluctuations in production volumes and changes in specifications as requested by customers.
-
Production plan creation
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
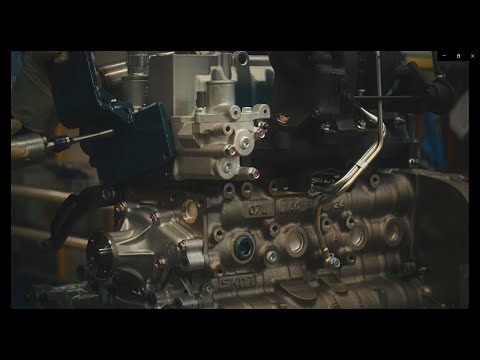
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Part selection
-
-
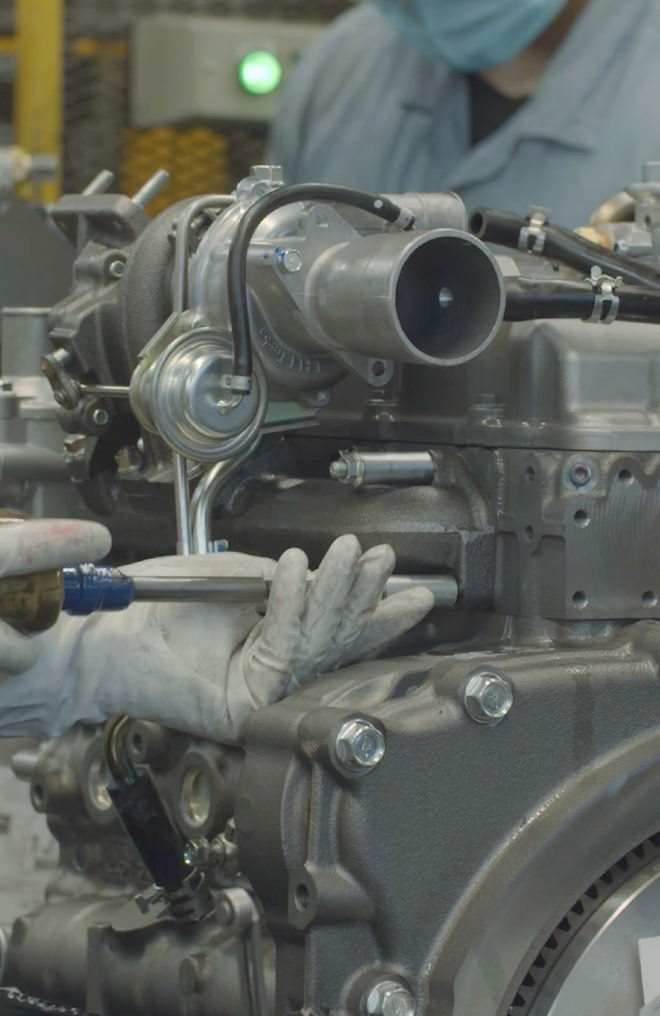
-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Assembly
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Cylinder head assembly
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Defect prevention device
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Nutrunner
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Torque check
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Traceability
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
Leak test
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
DPF
-
-

-

Assembly
Production plan creation
We create an assembly order table, list the components required for each assembly line, and create a production plan.
This order table allows us to manage the complex steps required to assemble over 2,000 engine models.
-

Assembly
Part selection
We use barcodes to manage the assembly order table. When barcodes are read in engine component pick-up areas, lights light up in the locations where the components required for each engine are kept so workers can go pick them up. We also arrange Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in locations where they can be used to automatically carry components to the line.
-

Assembly
Assembly
The line displays assembly instructions for engines with different specifications on screens, thus enabling workers to accurately assemble different engines one at a time.
-

Assembly
Cylinder head assembly
This shows our automated cylinder head assembly process.
-

Assembly
Defect prevention device
Fool-proofing (poka-yoke) is a way of thinking and a method for creating a state where mistakes do not occur.
We carefully designed the Kubota engine assembly line, which produces a wide range of products in small quantities, to prevent assembly errors. The correct components must be attached to engines carried along the line at each specific step before the engines can advance to the next step. For example, in our Sakai Plant, we have installed fool-proofing devices in approximately 200 locations and introduced mechanisms to ensure that workers are only able to use the correct components and tools.
-

Assembly
Nutrunner
We have implemented nut runners in the assembly process that tighten all joints with nuts at once.
This video shows the joining of crankshafts to cylinder heads.
-

Assembly
Torque check
We check torque values on the line during the assembly process. Each and every engine is carefully inspected to see whether it has the required torque values. We also check the tools workers are using.
-

Assembly
Traceability
To manage engine performance, exhaust gas response, and safety, we have set regulations for each factory and carry out traceability according to strict standards for things like nut runner tightening record traceability and injection timing traceability.
-

Assembly
Leak test
After assembly, we place engines in water to check for leaks.
-

Assembly
DPF
At Kubota, we also manufacture DPFs in-house, which are very important components in emission regulations around the world. At our Sakai Rinkai factory, workers assemble components while riding on Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
-

Assembly
IPU
Injection Pump Units (IPUs) are components that send fuel into diesel engine combustion chambers at high pressures. Kubota has also created an independent line for producing these components in-house for mounting in its V3 Series of Kubota engines.
IPU
-
Kubota INNOVATIVE METHOD
Kubota's uniquely consistent
production system,
featuring innovations
unlike any in the world