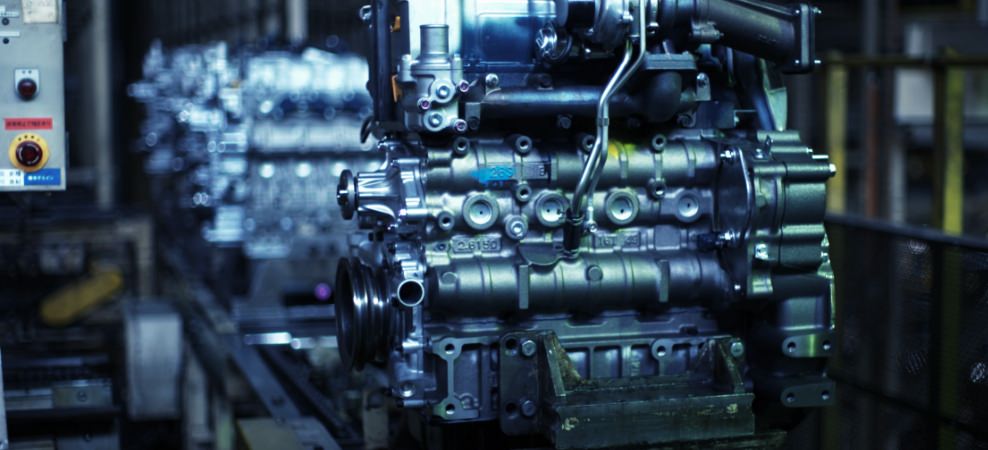
Casting

The Magma of Creation Produces Supreme Performance Imbued with Wisdom
The crankcase is the most important part of an engine's framework. It includes most of the engine's 1,000 parts.
It has many crevices, and requires irregular, ultra-complex, high-precision shapes, toughness, rigidity, and high dimensional accuracy.
Kubota manufactures high-quality crankcases by making full use of casting production technology which has been cultivated over the 100 years since the company's establishment in 1890.
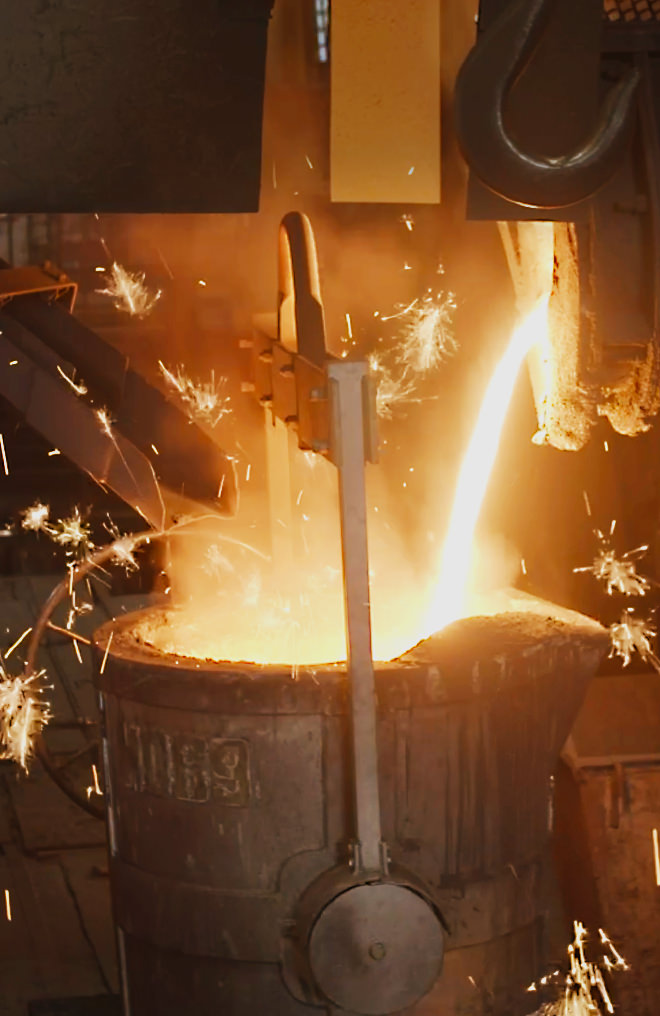
Casting is a molding method that melts metals at high temperatures and then pours them into molds in a hot liquefied state to create desired shapes and thus enable the production of even complex shapes.
The production of Kubota engines, rated as compact with high power output, is only possible because they are imbued with the wisdom of our 100 years of casting technology.
Kubota Engine's Crankcase Casting Lines
ES (Airflow Press Molding) Line
This is a casting method in which molten metal is poured into a foundry core molded into a crevice in the shape of a crankcase to form a casting. Most of this process is now automated to produce high-quality engine castings.
-
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Air impact molding machine
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Core setting machine
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Automated pouring machine
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Product picking line (manipulator)
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Automatic casting burr removers
-
-

-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic coating machine
We automatically paint the "foundry cores" that become crankcase molds to stabilize their quality.
-

Casting
Foundry-core automatic assembly line
We assemble these "foundry core" crankcase molds automatically. We stabilize the dimensions of complex structures so we can mass produce high quality crankcases.
-

Casting
Air impact molding machine
We use the air impact method to form the casting sand of foundry cores at uniform pressures. By using net shaping technique, we achieve thin walled products with high dimensional accuracy. We visually confirm that molds do not break when molten metal is poured in.
-

Casting
Core setting machine
We use automatic core setting devices to improve the dimensional accuracy of our crankcases.
-

Casting
Automated pouring machine
This is a pouring operation that pours metal into molds in a hot liquid state.
Kubota uses triangular ladles with shapes suitable for automatic pouring to save labor in pouring operations.
-

Casting
Product picking line (manipulator)
This is an operation that flushes molds to remove molded castings. Kubota uses a heavy machine called a manipulator to free workers from heavy work and heat.
-

Casting
Product boxing and automated warehousing (SA storage)
Our unique SA box method is a self-annealing method with excellent moisture retention properties that cools slowly using residual heat from products. This method cools molds from top to bottom in 8 hours.
It also saves energy and shortens lead times.
-

Casting
Automatic casting burr removers
Molten metal that flows out through gaps between molds solidifies into thin extraneous bulges called casting burrs.
We have introduced "automatic casting burr removers" to remove these burrs. They automatically find rough spots on products and clean casting burrs from product surfaces.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After removing casting burrs, we give products their final finishes by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
Shot blasting
-
LFP (Lost Foam Process) Line
In this method, a pattern the same shape as the product is made out of expanded polystyrene. This pattern is then placed in dried sand and molten metal is poured into it, resulting in the pattern melting away and being replaced by the molten metal to form the casting. This makes it possible to produce products with complex shapes without any burrs.
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Coating (first time)
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Drying (batch furnace)
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Coating (second time)
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Drying (continuous furnace)
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Molding and pouring
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Shot blasting
-
-

-

Casting
Coating (first time)
Our LFP line is used as the production line when casting crankcases with more complex shapes.
We apply refractory material to extruded polystyrene foam models with the same shape as the products.
-

Casting
Drying (batch furnace)
We dry the models coated in refractory material in a batch furnace.
-

Casting
Coating (second time)
We apply more refractory material to the models after they have been dried in the batch furnace.
-

Casting
Drying (continuous furnace)
We use a continuous furnace to dry models after their second coating.
-

Casting
Molding and pouring
We shape the models that have finished drying in the continuous furnace into molds and pour molten metal directly into the shaped molds.
-

Casting
Shot blasting
After pouring the molten metal, we give the molded products their final finish by shot blasting them with small iron ball-shaped projectiles.
-

Casting
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
After shot blasting, we inspect products for appearance, omissions, and dimensions.
Inspection (appearance, omissions, dimensions)
-
Kubota INNOVATIVE METHOD
Kubota's uniquely consistent
production system,
featuring innovations
unlike any in the world