features
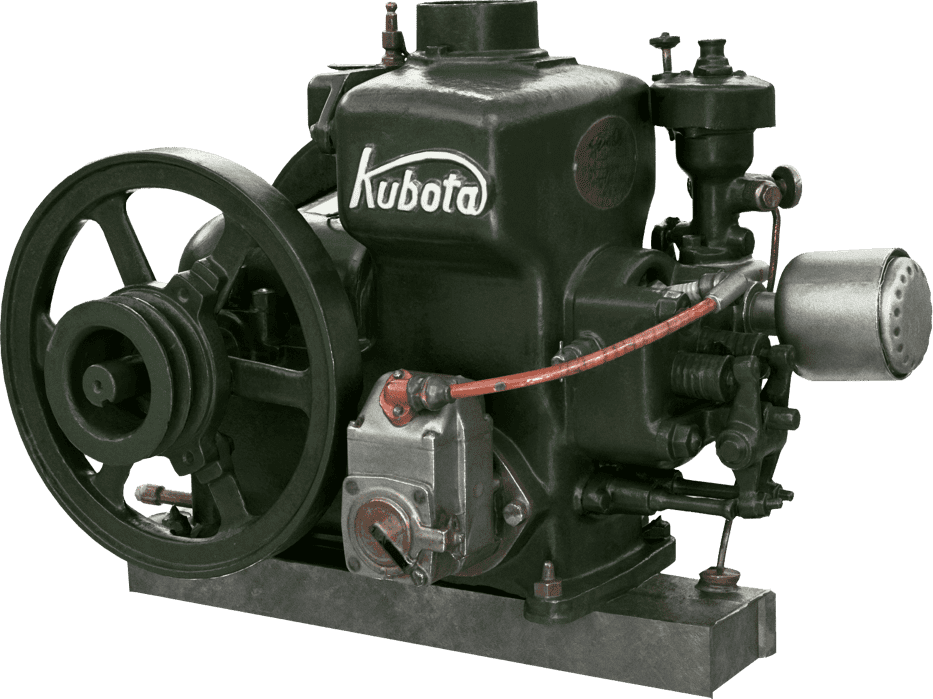
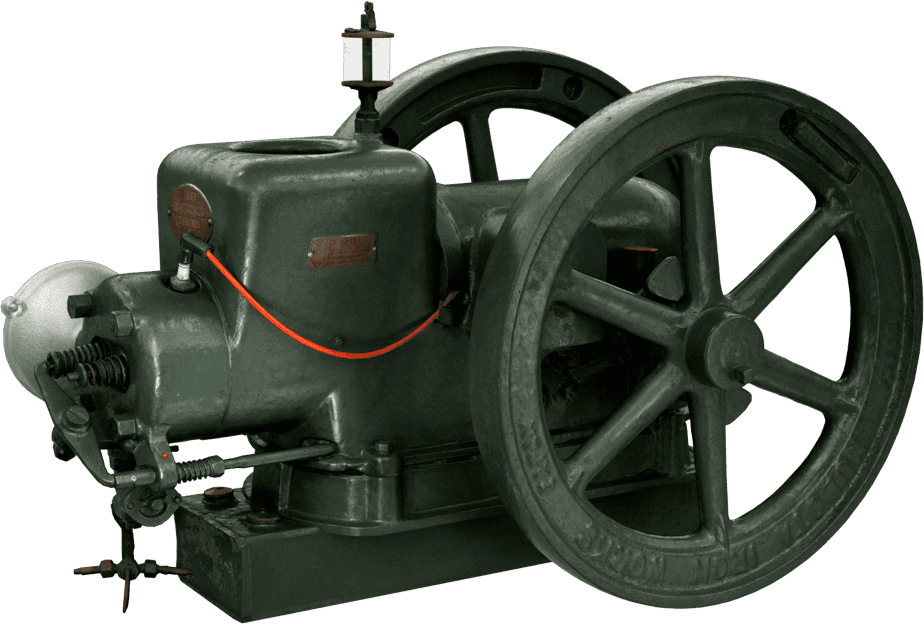
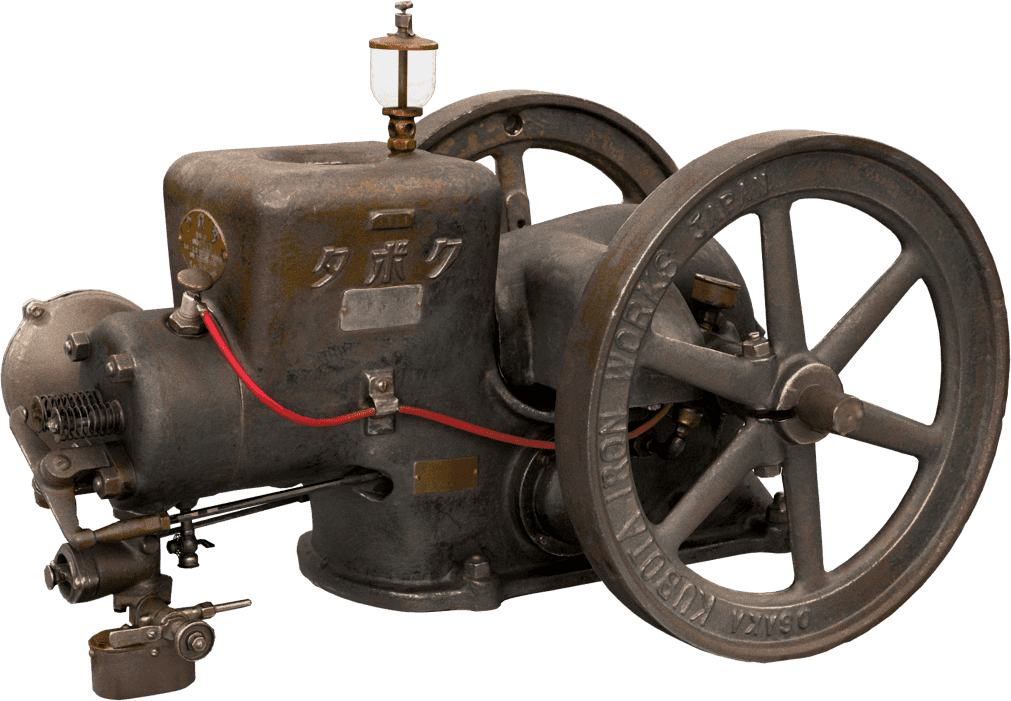
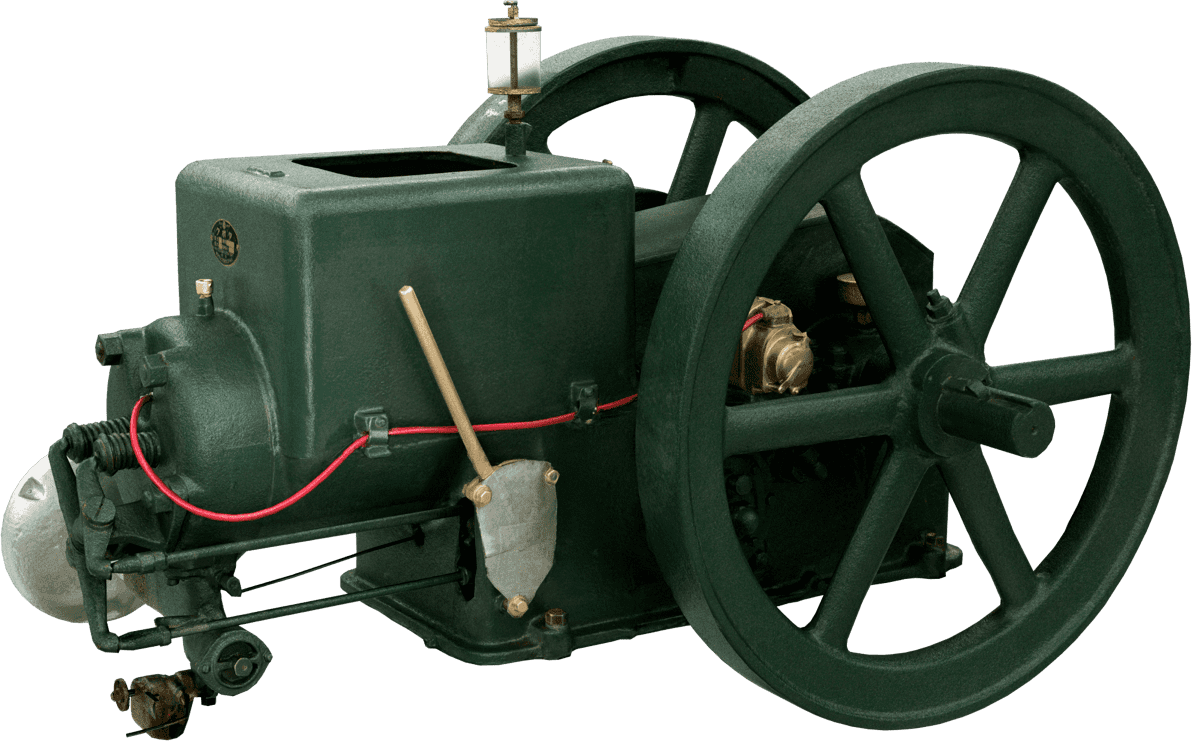
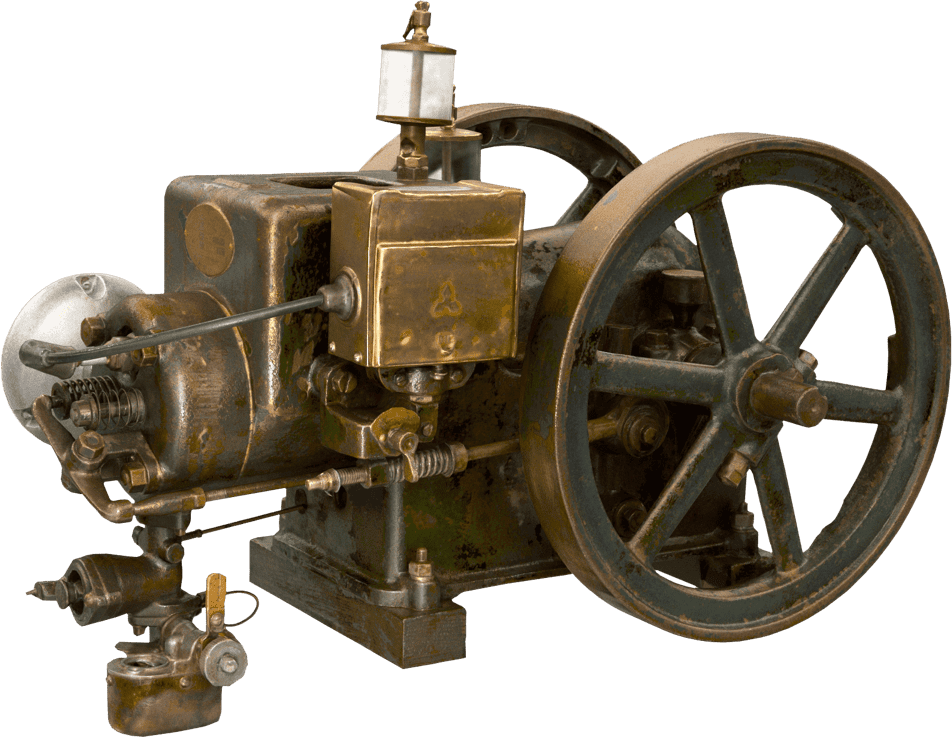
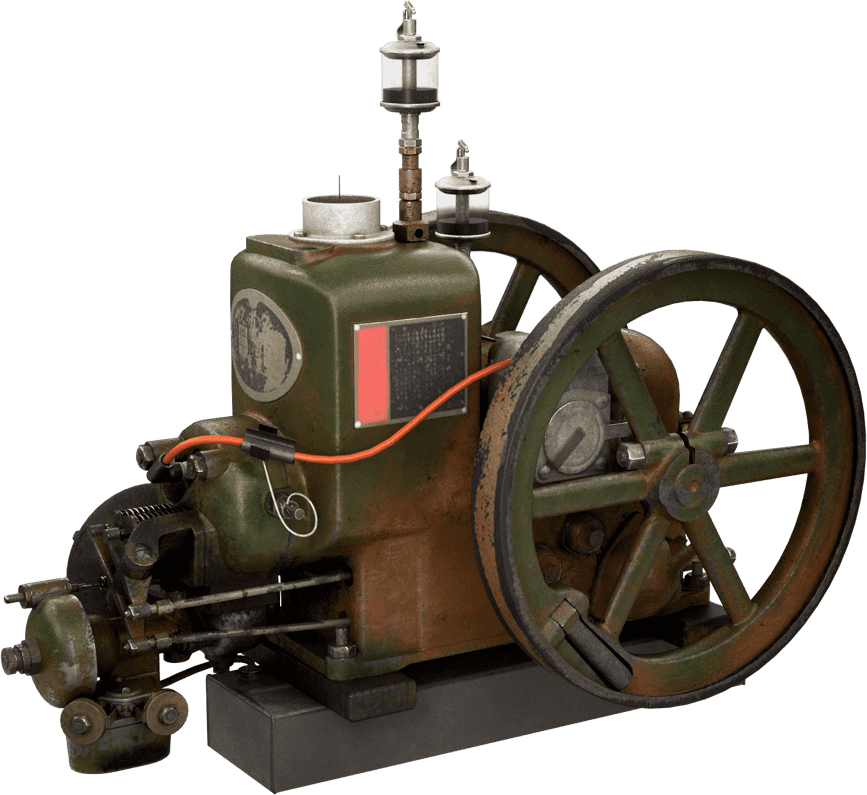
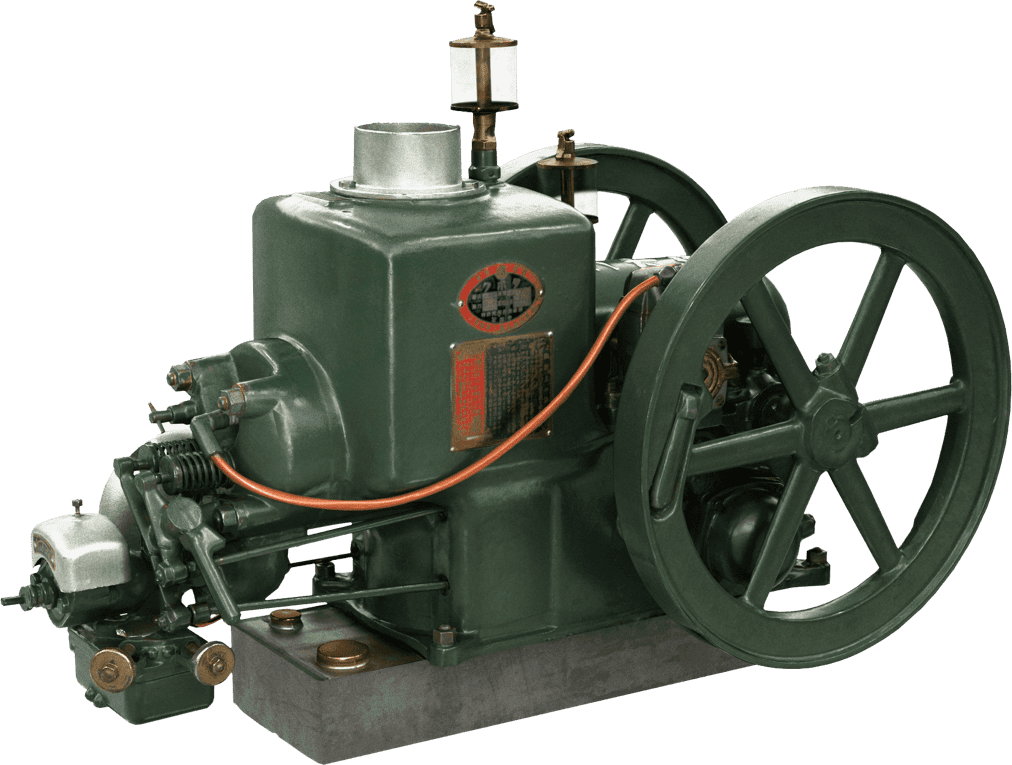
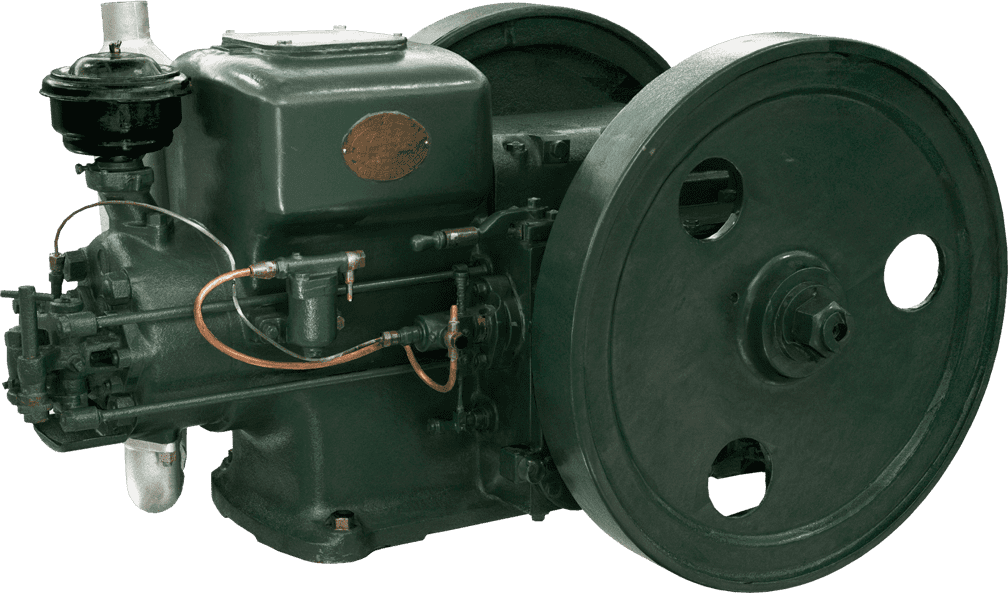
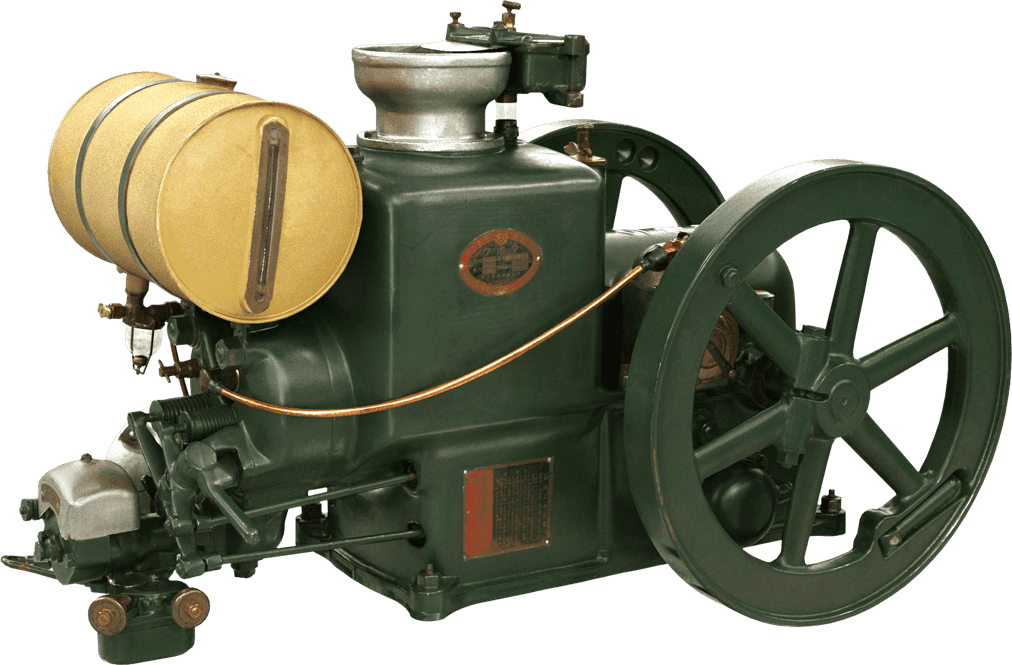
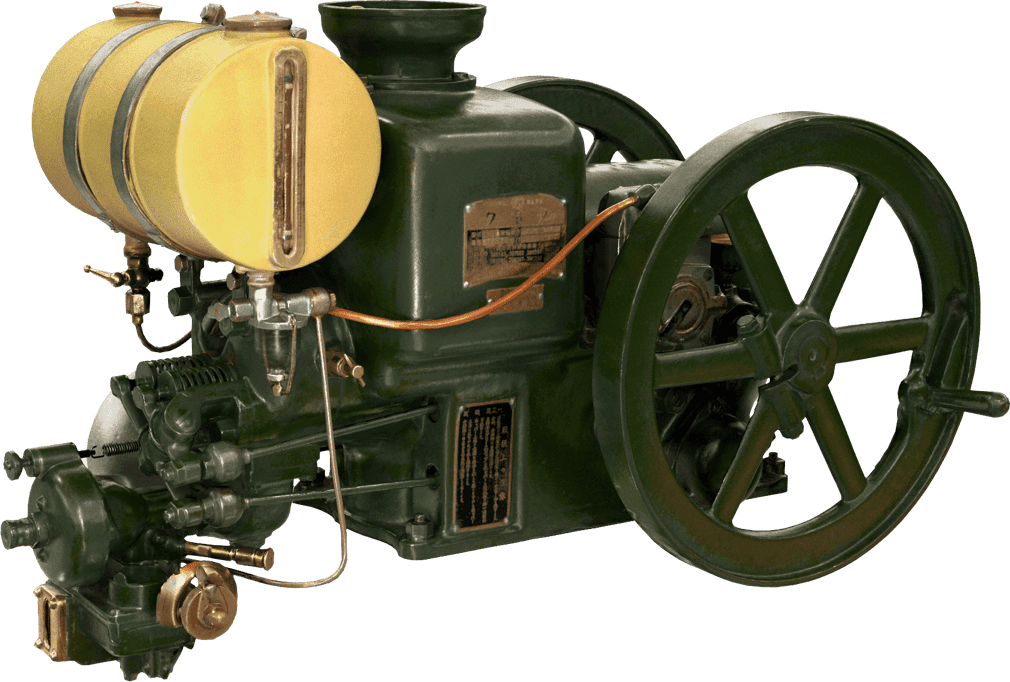
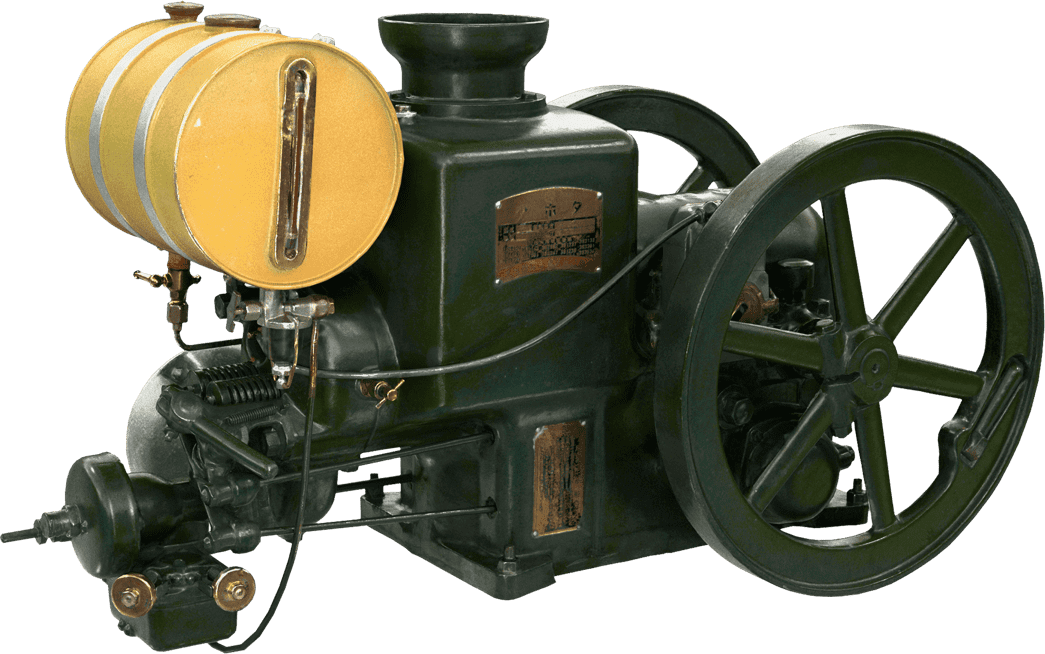
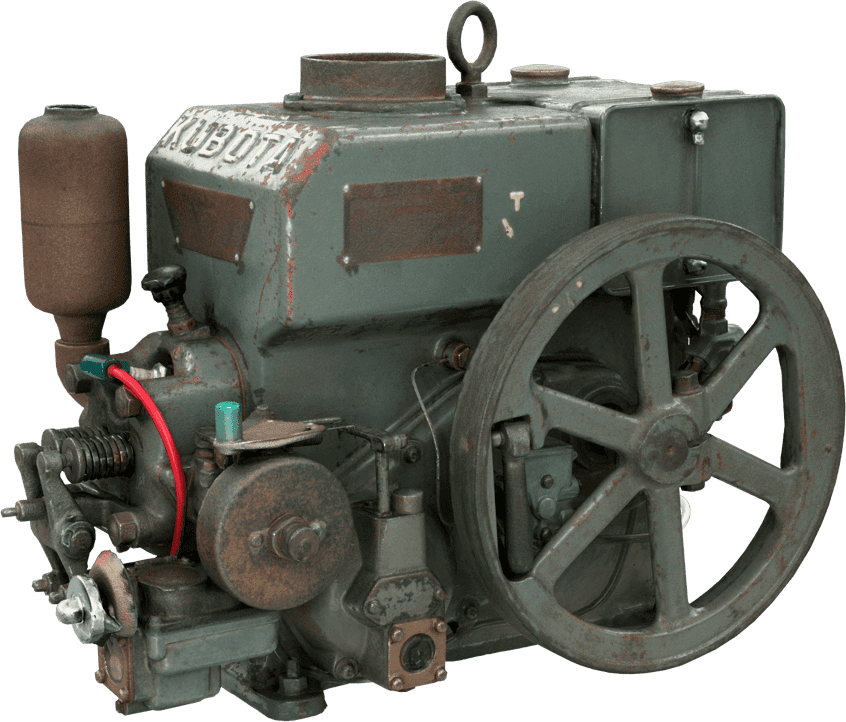
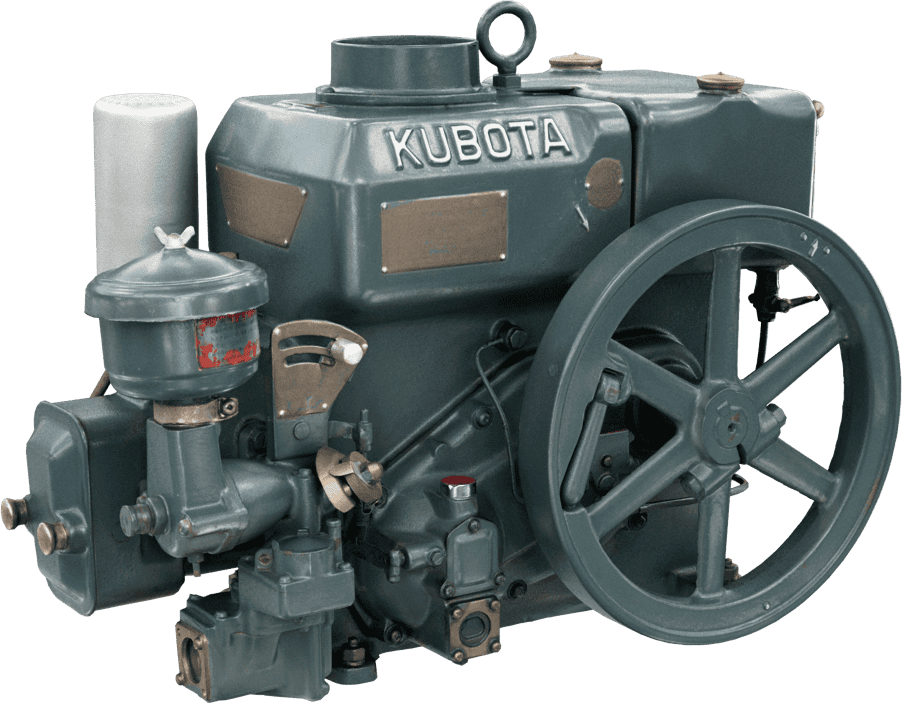
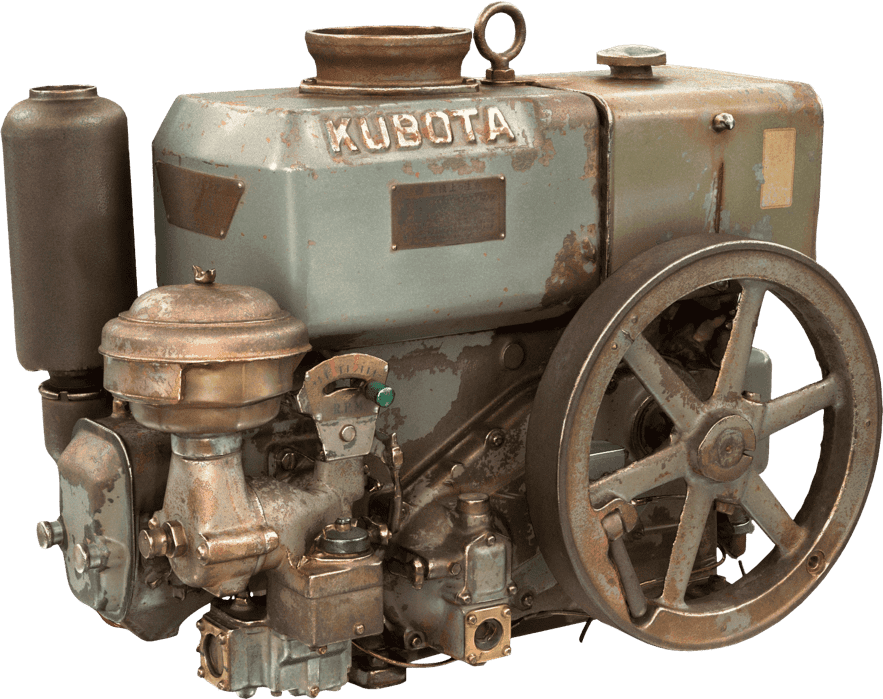
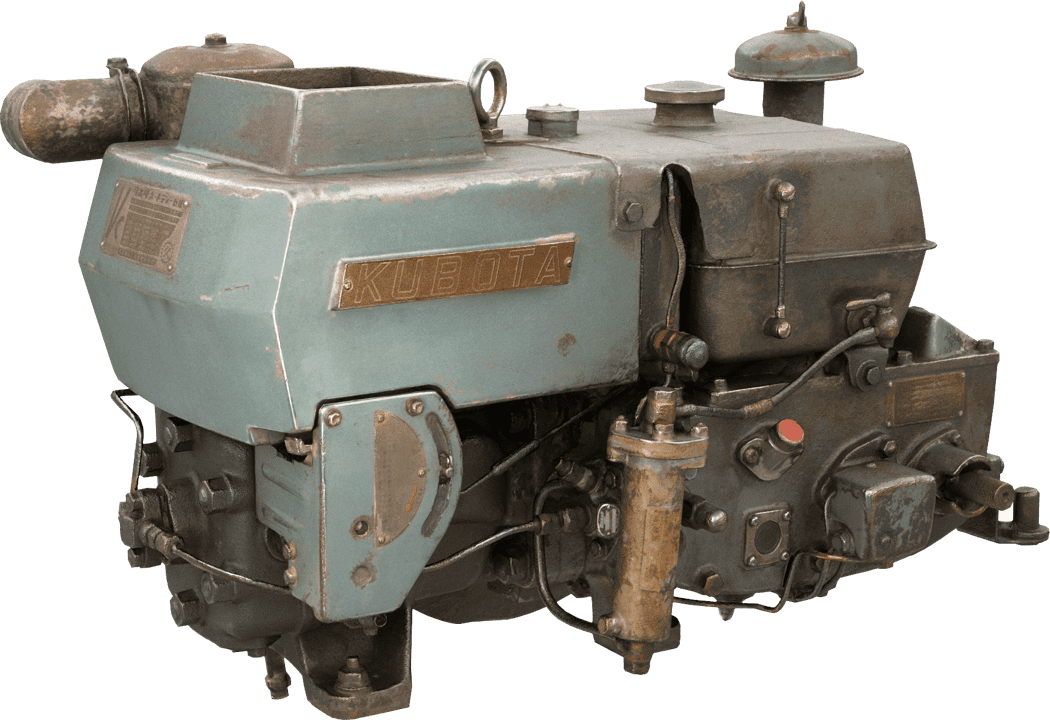
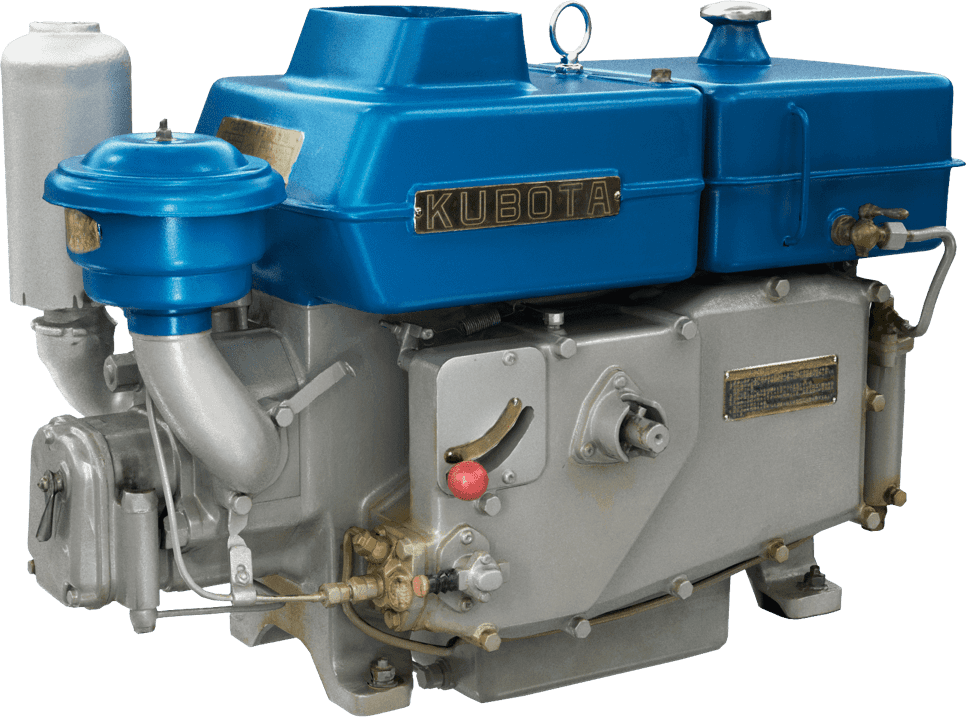
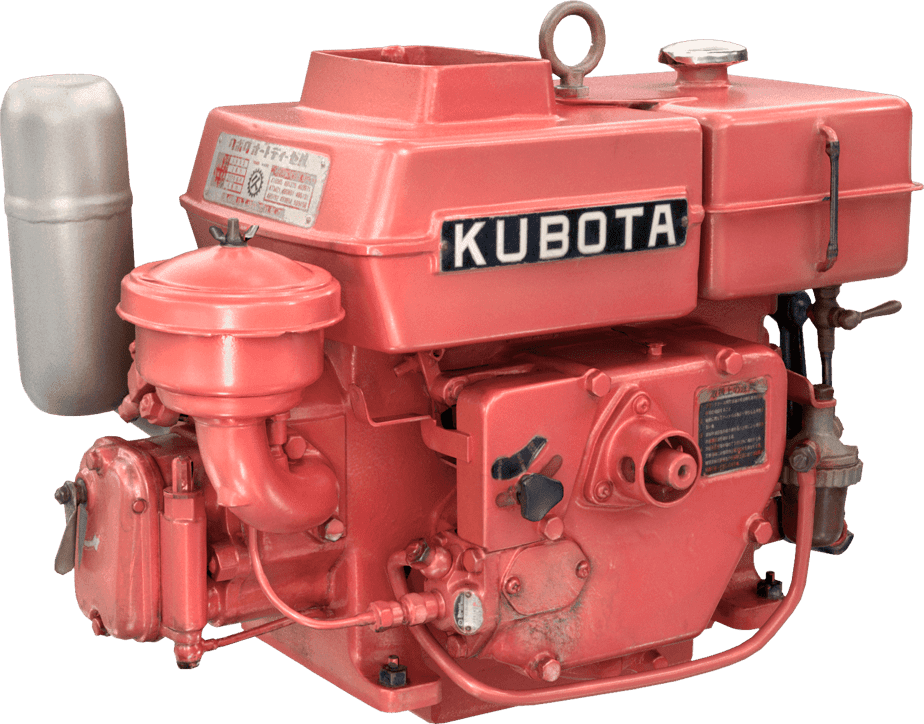
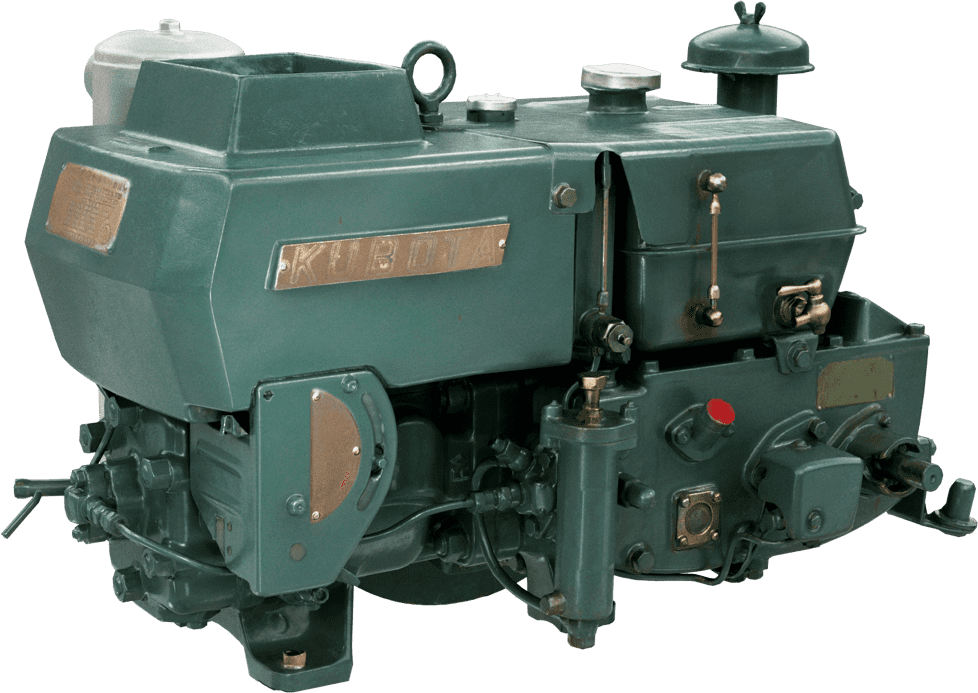
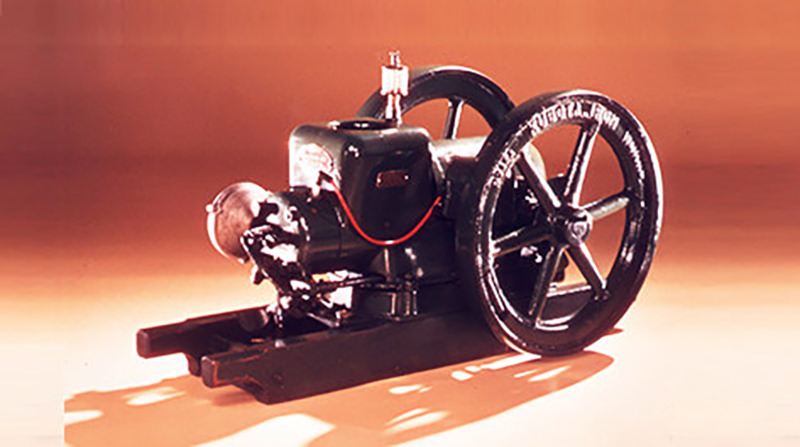
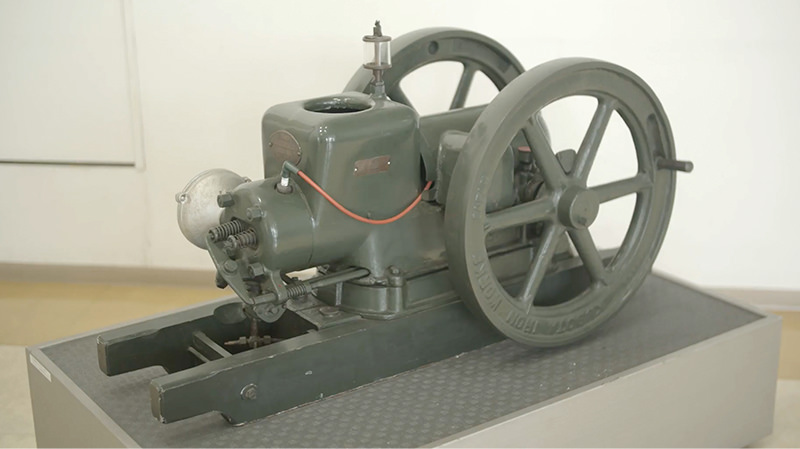
Kubota's First Engine
A launched in 1923. Production started with just a single model, before moving on to produce 2.5 and 3.5 horsepower models.
Kubota began manufacturing oil engines in 1922, the year a major drought struck western Japan.
The company determined that the production facilities and manufacturing technology of the machinery business, which was devastated by the recession, could be used to manufacture oil engines.
Heritage of Industrial Modernization, Japan
This engine is listed as cultural "Heritage of Industrial Modernization," a designation certified by the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. (Fiscal 2008, "2. A collection of the heritage of industrial modernization that illustrates the development of steam and internal combustion engines supporting a wide range of industries from heavy industry to agriculture, forestry and fisheries.")
specification
- Year
- 1922
- Fuel
- Petroleum
- Type
- Horizontal, water-cooled (low speed)
- Cylinders
-
- Number of cylinders
- 1
- Rated output / speed
- 3/400
applications
-
Rice Husker
-
Pumping / Irrigation Machine
-
Drilling Machine
story
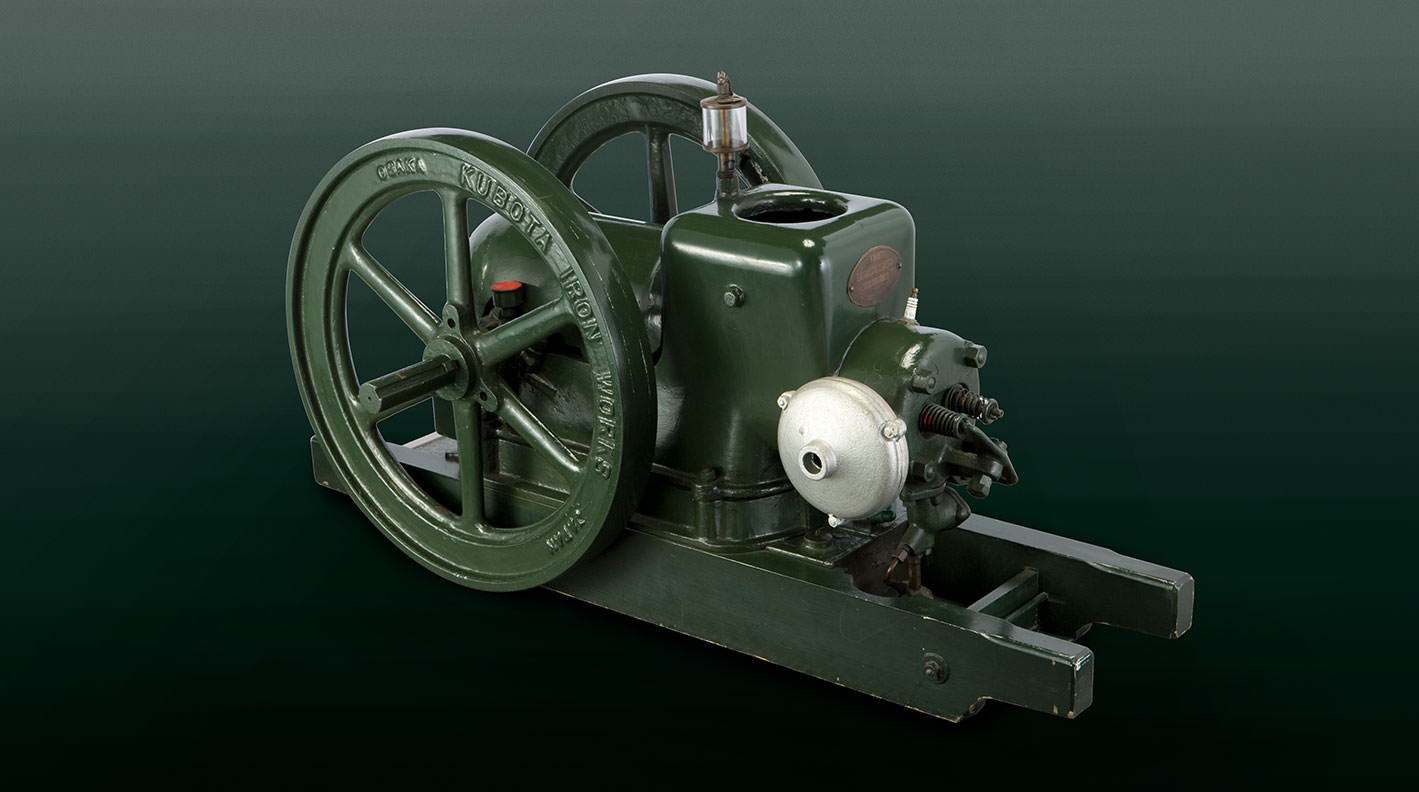

Why Did Kubota Start Making Engines?
Having established itself as a manufacturer of iron pipes for waterworks and expanding its business, Kubota was looking for new opportunities. The company's automobile manufacturing business continued to stagnate and they were looking for a way to break out.Also, at that time, the post-WW1 recession combined with a drought took a heavy toll on both Japanese industry and agriculture.It was here that Kubota faced a major turning point.
review
Ranked highest in comparative examinations by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan
Photos
Discover other engines