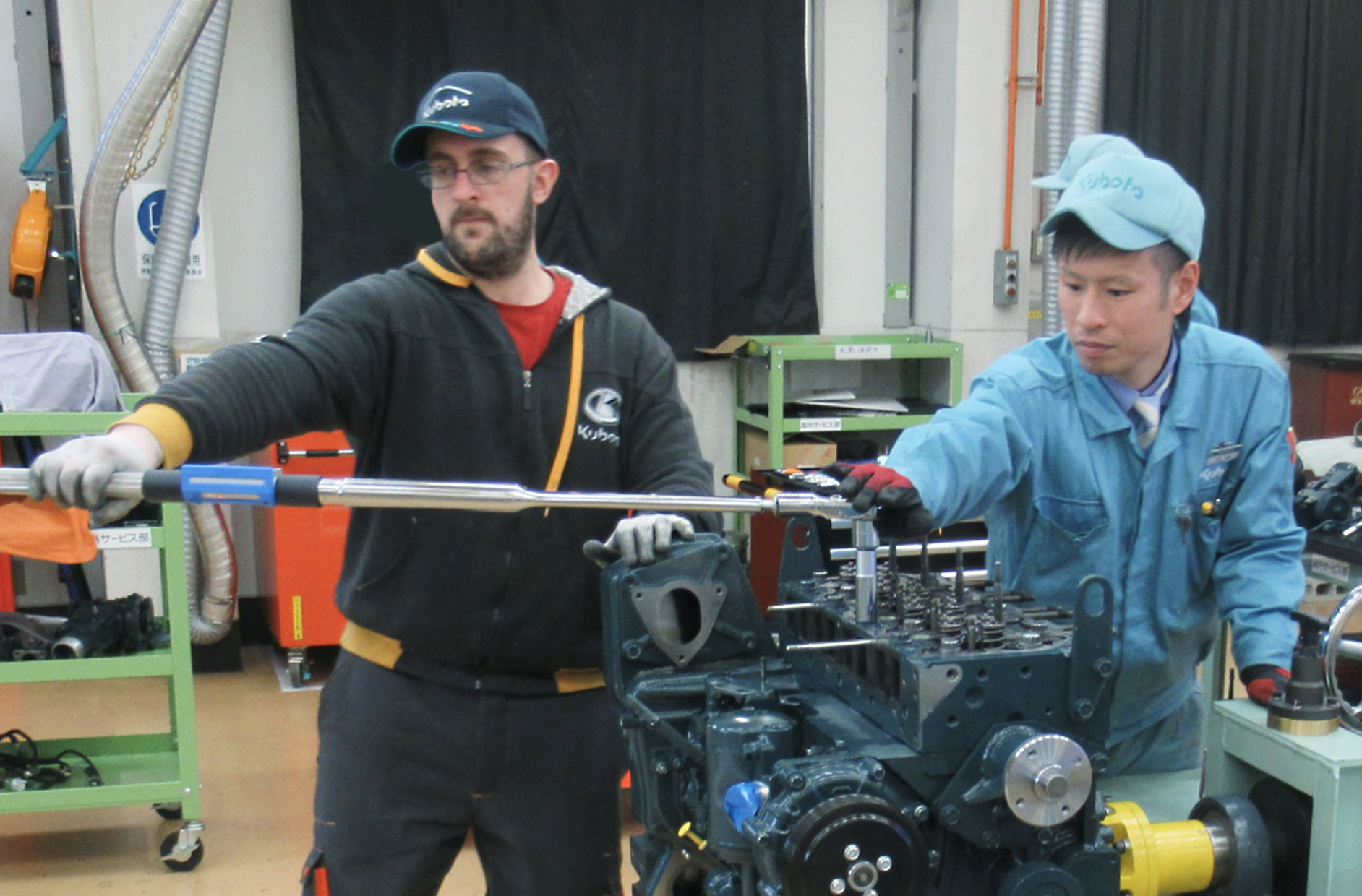
One Service Worldwide
Kubota doesn't just produce engines — it also provides after-sales services for OEMs, end users and other actual engine users.
Kubota believes that once a Kubota engine has been installed as a power source for industrial machinery, after-sales service, including quick and accurate servicing and repair, as well as the provision of service parts, is very important for the long and reliable operation of the engine.
Kubota's engine service aims to maximize and maintain the performance of Kubota engines installed in OEM products, and to ensure rapid recovery in the event of a breakdown, all with the goal of satisfying our customers.
Engine Service Department is responsible for servicing. It provides service-related information and reference materials to, conducts training with, and responds to relevant inquiries from Kubota sales companies. Each trained Kubota sales company also trains its distributors and dealers that actually provide servicing to engine owners. This service linkage is the Kubota Engine Service Network.
The Engine Service Department develops and operates the Network, creates service documentation for the engines, provides training to the trainers from Kubota sales companies who train Servicing Engineers, develops diagnostic software, establishes product traceability. It also conducts proof-of-concept tests using the latest technologies.
The Engines serviced by Kubota are an important component of our customers' arsenal.
That’s especially why there is Kubota Engine Service's Service Vision: We aim to create more and more Kubota fans by continuing to focus on customer-first and worksite-oriented principles, providing one service worldwide that provides peace of mind and inspires our customers.
The History of Kubota's Engine Service
From around 1947, the free trade of agricultural machinery in Japan became more active, and it became necessary for Kubota to review the sales system for their engines.
Up until then, Kubota's engines had been sold by the agents Sugiyama Shoten (Kubota trademarks) and Mitsubishi Corporation (Tobata trademarks). However, Kubota came to the conclusion that if they wanted to expand the distribution channels for their engines and work toward extending the reach of their products, they needed to establish a sales system that was unique to them, whereby they could control everything from manufacture to sales and service. To this end, they stopped using agents and instead switched to a dealership system.
At the same time, Kubota needed to build its own service network and train its users in how to use, service and maintain their engines.
Kubota switched to this unique sales system in 1948.
To improve servicing and training, Kubota opened a technical workshop in 1949, and started running technical courses.
In 1952, Kubota built accommodation for the Servicing Engineers attending the training, and made improvements to the content that was taught on these courses. Then in 1957, Kubota built an overseas training center for trainees from abroad.
Kubota's engine services were established to fulfill the important role of communicating about the correct use and maintenance of engines to Kubota users and dealers. To this day, the content and scale of the training are continually being expanded to stay up to date with current needs.
Working Toward Meticulous Training Services
Kubota has established the Kubota Engine Service Network (KESN), which consists of Kubota, sales companies, distributors and dealers, and forms the basis of Kubota Engine's service offering.
The Engine Service Department develops trainers from sales companies, and the trainers train Servicing Engineers at affiliated distributors and dealers.
This training helps Servicing Engineers to provide support to OEMs and end users with regard to proper servicing and repairs.
In addition to regular training, training is provided when new engines are introduced to the market.
When a new engine is put on sale, Engine Service Department works with Engine Engineering Department to create training programs, develop training materials, and train the sales company trainers who support KESN in that region, in accordance with sales plans.
Training is conducted at the internal training facilities of
Kubota and Kubota sales companies.
The training covers everything from disassembly and assembly of
engines to troubleshooting procedures.
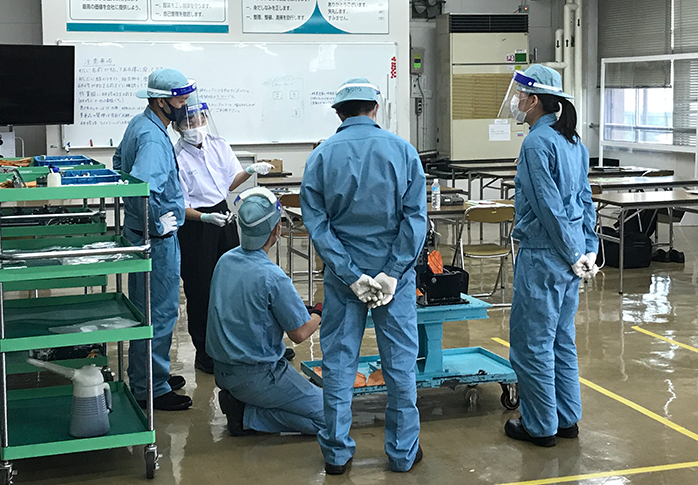

In-person training over a couple of days that involves working on a real engine helps engineers better understand the engine, leading to a high quality of service.
Leveraging Online Training, eLearning, Videos and More
Kubota's diverse array of engines is part of what sets it apart. There are a number of engine variations, including minute differences between displacement settings and fuel types. To reflect all these variations, the Engine Service Department has prepared training programs for every type of engine.
Training has been formulated to explain the basic points that are common across all of Kubota Engine, and we have also designed specific training programs that efficiently explain the differences between each engine variant.
Kubota is also working to improve the quality of our training, by introducing an eLearning system and online video content that can be used globally, as well as training benches that simulate the movements of real engines for inspection.
In addition, Kubota has expanded its online training, and is improving its training system by cooperating with sites in other regions.
We also believe that Kubota needs to develop Servicing Engineers, and so we provide a training curriculum for beginners who are new to the engines.
In response to many diverse types of Kubota engine, the Engine Service Department are undertaking various initiatives to increase the satisfaction of each and every customer, with the aim of providing one service worldwide.
Kubota Engine Park (KEP) Gathers Engine Information for Each and Every Customer
Kubota Engine Park (KEP, formerly K-iSS) is Kubota's website for partners to find technology, parts, services, maintenance and other information related to Kubota engines.
It is a huge database that compiles information for every type of engine, and it can be viewed over the Internet by sales companies, distributors and Servicing Engineers at dealers.
Kubota regards traceability very highly throughout the product lifecycle of manufacturing, shipping and market services, and maintains a product history using serial numbers assigned to each unit.
For example, if an user contacts Kubota regarding a malfunction or an abnormality, the Servicing Engineer can look up all engine information, documentation and parts information by searching for that engine's serial number.
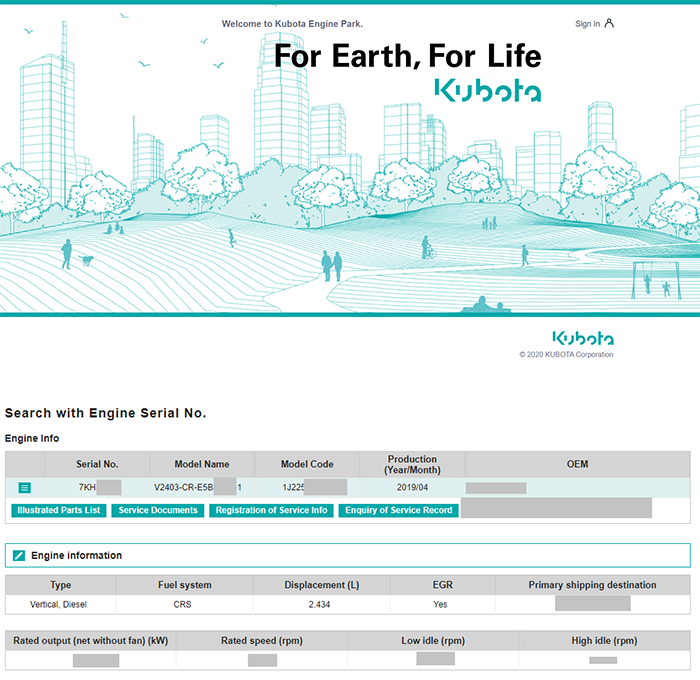
It will then display the repair manual, the diagnosis manual and the parts list for each engine. Of course, the manuals are available in multiple languages. This allows the Servicing Engineers to quickly retrieve information about the engine and immediately respond to end-user queries.
In addition, some electronically-controlled engines have components that require a service history.
Engine Control Units (ECUs), which controls the engine, are also given unique serial numbers. KEP displays information such as which version of software is written to each ECU, and their service histories.
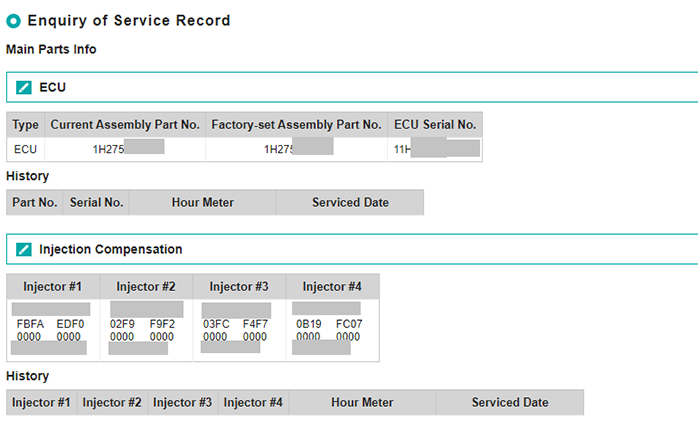
Common rail engine injectors have correction values for each cylinder. These correction values must be recorded correctly in the ECU to guarantee emissions performance, so both the data configured during manufacturing and the injector correction values for when they are replaced on-site are recorded.
To put it simply, KEP keeps track of all the technical information and service histories for the engines used in each customer's industrial machinery.
Information about Kubota engines in operation all over the world is compiled here, and this information is evolving every moment.
Diag Master, the Engine Health Diagnosis Tool
The Engine Service Department also develops some diagnostic software for Kubota engines. When common rail engines were introduced in the late 2000s, Kubota adopted the diagnostic software Diag Master to troubleshoot engines using a PC.
Connecting a PC with Diag Master installed to an ECU makes it possible to capture digital signals emitted by the ECU, such as power output and speed, and for the status of those signals to be displayed on the Diag Master interface.
If a malfunction or an abnormality is detected, a fault code is displayed, enabling the user to quickly troubleshoot the fault.
In addition to diagnostic software for common rail engines, Kubota has also developed and introduced the KGST (Kubota Gasoline Service Tool), a diagnostic software tool for gasoline engines.
This diagnostic software allows engines to be diagnosed directly by an on-site Servicing Engineer, and then the appropriate course of action can be taken after viewing the diagnosis manual on KEP.
End Users Can Manage Maintenance Information on Their Smartphones Using the Owner's App
Engine Service Department has also released an app called Kubota Engine Owner's App to enhance engagement with end users, which provides information about regular maintenance and dealers to users who register their products.
The Kubota Engine Owner's App is available on smartphones, and the end user can register any engine that they own using a serial number. It is linked to the KEP database, and allows users to view engine operator's manuals, and includes, among other things, information about periodic maintenance, such as filter replacements and oil changes.
It is also possible to view KESN locations and search for locations that offer servicing.
Engine Service Department not only provides information through the app, but also obtains information about engines that are in use. This information can then be used to work out how to improve the quality of the service, such as where service locations should be set up in the future.
Kubota also plans to make some enhancements to this app. Kubota wants to improve the usability and usefulness of information, understand the needs of its diverse range of users, and then develop more specific services based on these needs.
Research into Next-Generation Services Such as Learning in Virtual Reality (VR) and Working in Augmented Reality (AR)
Engine Service Department has introduced supplementary systems for servicing that use the Internet, PCs and smartphones to view and share engine information, such as KEP, Diag Master and the Kubota Engine Owner's App, and we plan to introduce more new technologies in the future.
Specifically, Kubota plans to leverage VR and AR to improve the quality of its services.
Engine Service Department is researching technologies that use VR and AR technologies to visualize things that are not there in real life, and things that are there but not visible.
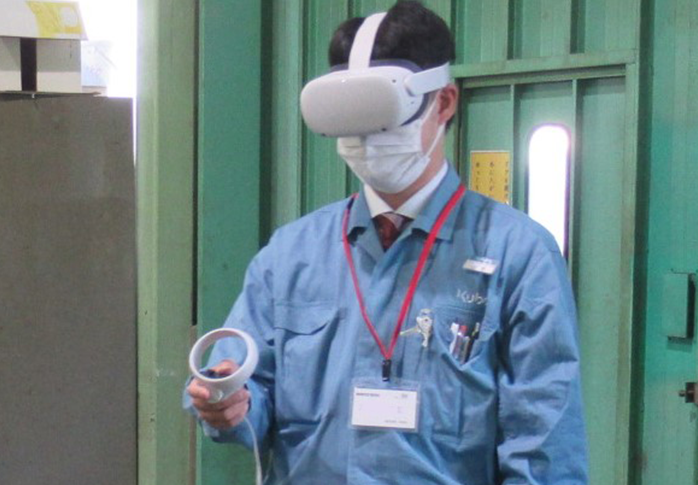
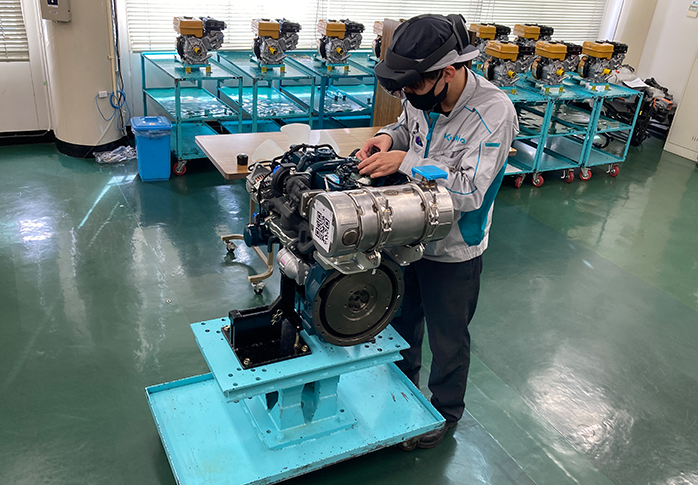


VR is used for training on new engine models.
VR stands for "virtual reality," a technology that uses specialized eyewear to view 360 degrees of imagery that covers the entire human field of view, giving the wearer the feeling of actually being in that space. It gives users the feeling of being able to see and control things that aren't actually in front of them.
Kubota is researching technologies for projecting and visualizing things that cannot normally be seen, such as the flow of air and electricity, onto real engines.
For example, Kubota uses 3D models for its current engine development, and a Servicing Engineer wearing a VR headset can use these 3D models to learn about engines and simulate their disassembly.
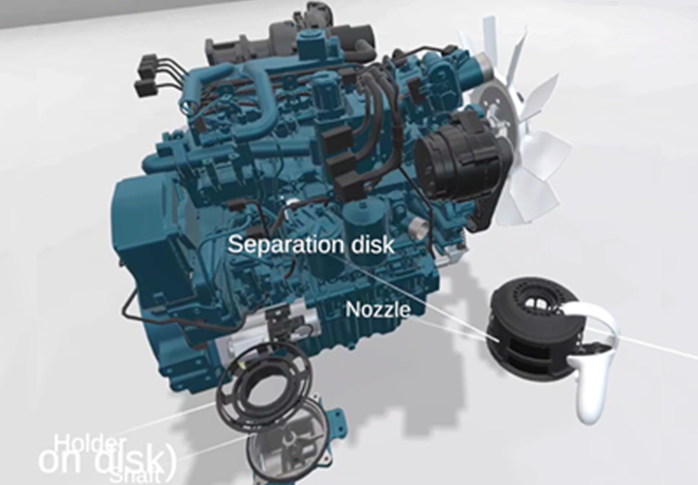
When this technology becomes generally available, there will be less of a need for Servicing Engineers in other countries to physically travel to Japan, so training can be completed quickly before a new model is put on the market.
AR is used as an aid when working on a real engine.
AR stands for "augmented reality." It expands the real
world by virtual means, by superimposing virtual visual
information onto real scenery and objects.
The AR technology being researched by Engine Service Department
is a dedicated AR wearable device for Servicing Engineers that
projects the information they need to address faults and perform
maintenance onto the engine in front of them. Servicing
Engineers can focus on the engine and still see instructions and
guides, rather than having to look back and forth between the
engine and a paper manual or PC screen, helping their work
progress smoothly and accurately.
For example, when installing a wiring harness for electronically-controlled engines, the device shows the correct way to fit the harness over the actual engine.
Fitting a wire harness is very complex and even experienced personnel must take great care to ensure that there is no leakage of current when disconnecting and refitting them.
In the current workflow, the operator fits the wire harness while looking at a manual or image, and must pause their work each time they look at it.
But with AR technology, they can perform each step of the
process in order using the guides displayed alongside the
engine, so they don't have to take their hands away from their
work, and they can complete the installation accurately and
quickly.
If this technology can be realized, it can be deployed in the
same way for jobs that require special care, such as managing
the tightening torque of bolts fastened at different points in
the engine. Working at the same time as reviewing the materials
is much more efficient and accurate.
While there are still some hurdles to overcome for full-scale introduction of VR and AR technologies, Kubota plans to drastically improve engine services as part of its digital transformation (DX) strategy for its engine business.
In order to ensure that people can continue to use Kubota engines for a long time to come, Engine Service Department will use its accumulated experience in training, and the technologies that are underpinned by that expertise, to work toward new initiatives to improve the quality of servicing and provide customers with peace of mind.









